Some time ago a Japanese colleague told me that the best energy efficiency standards of Japan were not even close to the lowest standards of Germany. And yet, Japan used a quarter of the energy that Germany used in heating.

Although I could not find the sources for any of those claims, the whole discussion seemed ill-focused, as when comparing tomatoes to potatoes: they have similar origin and sound quite close, but they are different things.
But, Japanese houses are cold, aren’t they?
Japanese houses are famously cold in winter, but life around the tatami room is a warm experience.
Instead of heating the whole house, or the whole room, heat is focused where needed, just by the table. Cold evenings are kept at bay under the kotatsu, where kids do their homework, parents work, the family enjoys dinner, and friends have a drink.
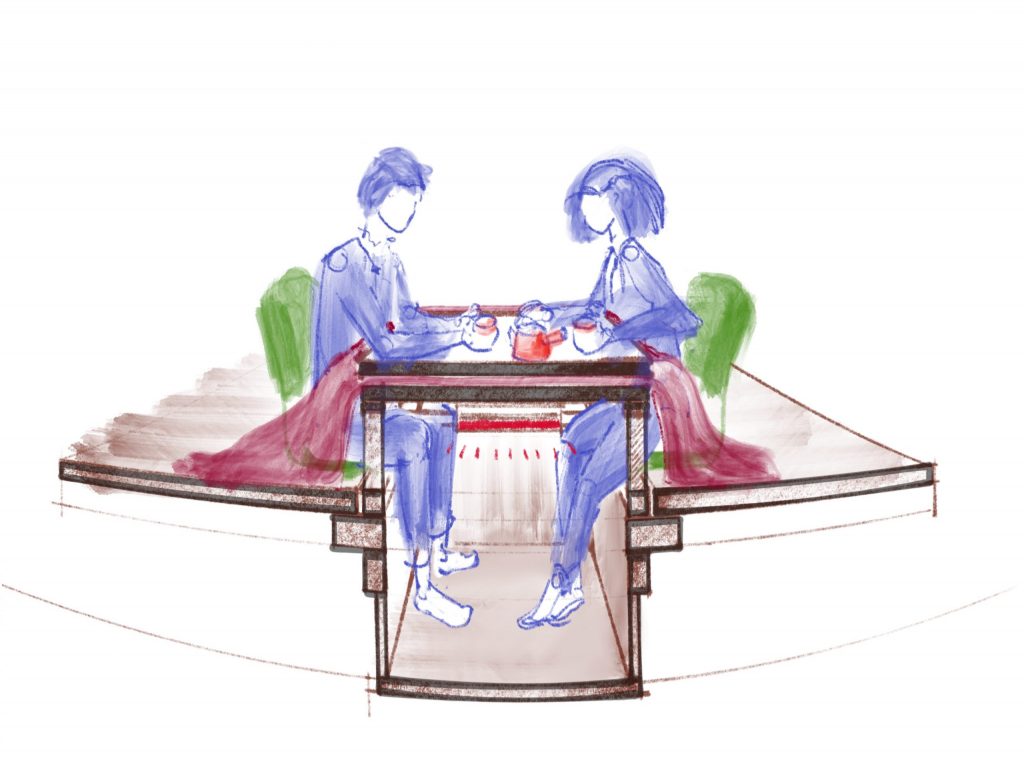
The kotatsu is a short-legged table with a heater attached to the underside, and covered by a blanket or a quilt. You sit at the table, and your legs are covered and warm under the kotatsu. The upper body is kept warm with the help of thick clothings like hanten (a kind of padded jacket). If you are planning to move in and out from the kotatsu frequently, a tanzen would be a better choice for clothing (it similar to the hanten but longer, covering the legs as well).
Thus, thermal comfort is achieved with a small heat source and proper clothing, which actually makes a lot of sense from an energy efficiency point of view. In Norway they say “There is no bad weather, there is bad clothes!” Is it really necessary (or even wise) to crank up the thermostat just to walk around in T-shirt?
OK, the tatami room gets nice and cozy with the kotatsu, but why are the houses so cold anyway?
We can find the reasons behind all this coldness in the way houses are built:
The first reason is, of course, earthquakes. Due to the constant seismic activity in the islands, the Japanese developed a light construction system with wooden structures, thatched roofs, tatami floors, and shoji partitions (paper over a wooden lattice).
Light structures are more resilient (less stress on the members), and shake and move with the earthquakes without snapping. (As an added benefit, if they do snap and fall over you, it is easier to crawl away from under light rubble.)
Then, humidity: Summers in Japan are hot and very humid, and structural wood, thatched roofs, tatami floors, and paper walls tend to rot very fast if they stay wet. Thus, the best way to prevent degradation is by allowing them to dry, which is achieved by good ventilation. This is, houses needed to be drafty.
Constant seismic activity also produces material fatigue on the structural members: minor cracks that appear at every cycle of movement. And after a while, the whole structure collapses. Unfortunately, repairs do not work well and there is no economic way to avoid material fatigue. For that reason, houses in Japan have had a pretty short lifespan (20 to 30 years), although constant advances in construction technology are pushing those numbers up nowadays.
The short lifespan brings another issue that impacts on energy efficiency: Upfront investment in insulation and double pane windows will not be paid off in lower utility bills during the life of the building.
Why is central heating so uncommon in Japan?
An efficient central heating system requires a properly sealed and insulated exterior envelope. And as explained above, that is not usual because it is expensive considering the whole life cycle of the building.
You may find air conditioners on several rooms of the house, but they will not be switched on all at the same time. Similar to the way Japanese use the kotatsu, they switch the air conditioner on only when they are using the room.
In sum, the tatami room is a nice example of flexibility and energy efficiency. Strategies for energy efficiency shouldn’t consider constructions as isolated systems, but as part of larger rhizomes that encompass not only climate and geography, but also habits and costumes, including furniture and clothing.